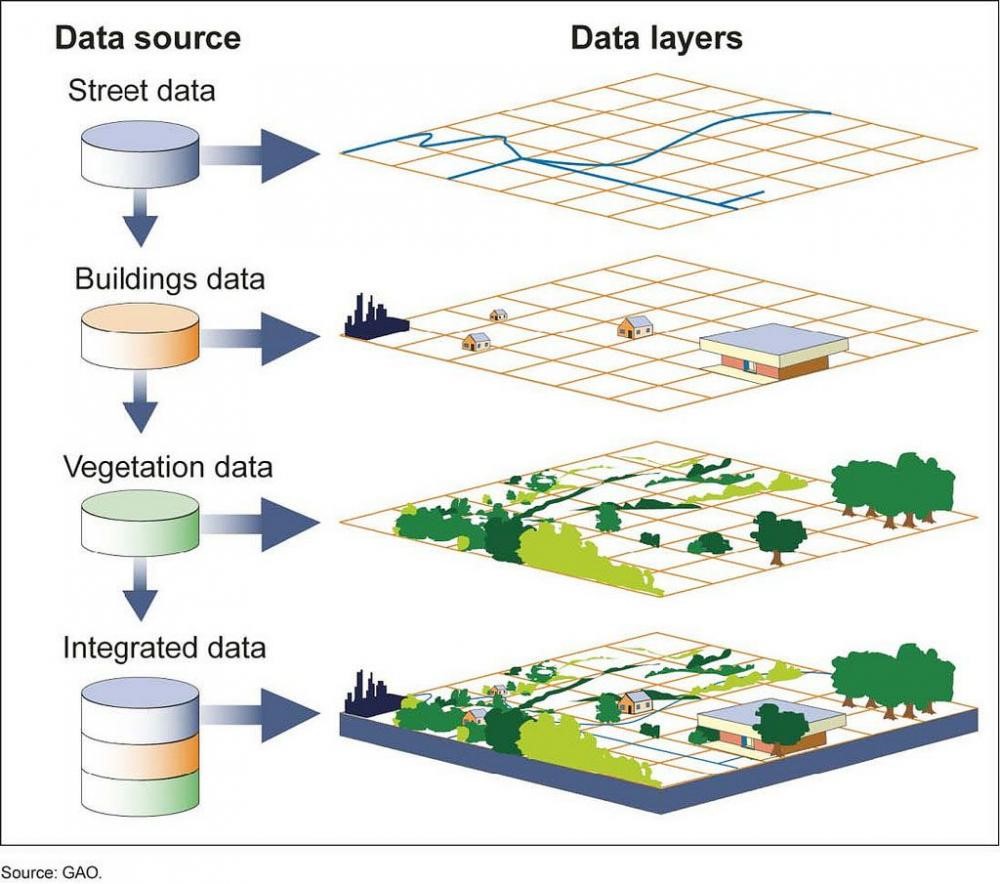
GIS (Geographic information system) software program helps to create, manage, analyze, and present geographical data in the form of maps including property lines maps, city mapping, land ownership maps, and parcel maps. GIS creates links between data and maps by fusing various forms of descriptive information like elevation, hydrography, boundaries, land use, and roads, with location data.
Table of Contents
ToggleThis paves the way for the creation of maps and the conduct of analyses, which are the two tools essential to site study in building design.
People can gain insight into geographical settings, relationships, and patterns with the help of GIS geographical mapping.
The Architecture, Engineering, and Construction AEC industry is increasingly using GIS to plan for the future. Using GIS mapping software can help you save time, improve communication, and engage more people in collaborative initiatives for urban planning, transport optimization, environmental analysis, and natural resource management.
Incorporating a project’s location into the design process can help ensure that the project’s context is understood and design solutions are provided for architects, town planners, and urban designers. Location intelligence changes how design and construction professionals plan, design, construct, and work in the built and natural environments.
Applications of GIS Mapping in Construction
- Identify problems: GIS data can be used to identify potential problems on a construction site, such as utility lines, environmental hazards, or unstable terrain.
- Monitor change: Through regular data updates and spatial analysis, GIS mapping enables construction teams to monitor and track changes in construction sites, such as land use, topography, or infrastructure development, ensuring accurate and up-to-date information for decision-making.
- Perform forecasting: By integrating historical and real-time data, GIS mapping enables construction professionals to forecast and anticipate future conditions or trends, such as traffic patterns or population growth, facilitating informed planning and design.
- Set priorities: GIS data can be used to set priorities for construction activities, such as which tasks should be completed first or which areas of the site need the most attention. It helps to identify geographic zones where the particular function of the building or landscape can align with.
- Understand trends: GIS mapping allows construction professionals to analyze spatial patterns and trends, such as landscape analysis, and traffic analysis, providing valuable insights for optimizing design and construction processes, improving efficiency, and identifying opportunities for design improvement.
Top GIS Mapping Softwares
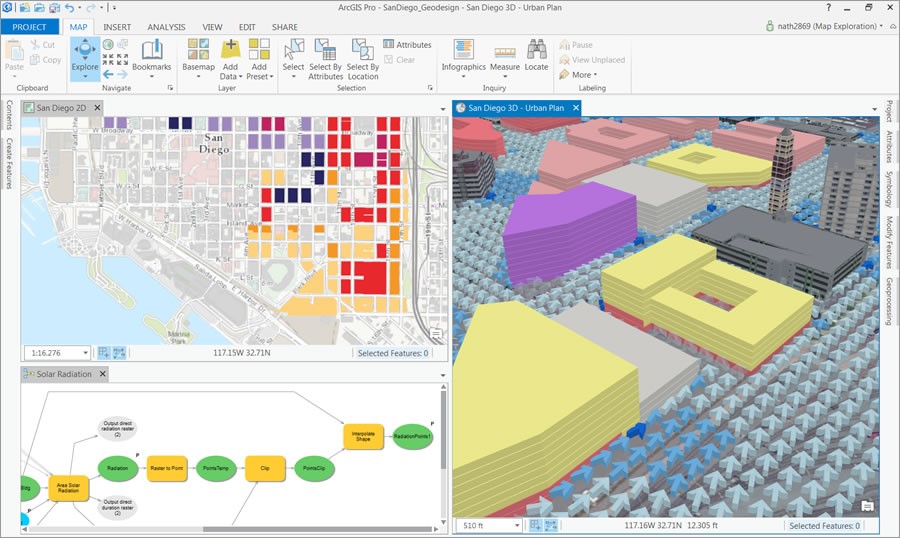
Esri ArcGIS
ArcGIS 3D GIS makes it simple to efficiently and securely collect, crowdsource, store, access, and share location data. You can instantly assess and solve problems, as well as communicate ideas and concepts with your team and building owners, by transforming your location data into smart 3D models and visualizations.
By highlighting geographical trends in your data, GIS property maps facilitate informed decision-making and prompt action while designing buildings and infrastructure in the context. ArcGIS Online enables architects and engineers to make, view, and share maps from any device.
Special features of Esri ArcGIS include:
- Integration: In addition to integrating desktop, server, mobile, and web applications, ArcGIS also offers extra tools and infrastructure for expanding the scope of GIS implementations.
- Geoprocessing: It offers a wide range of advanced geoprocessing tools and spatial analysis capabilities including buffer, clip, dissolve, intersect, union, and erase tools.
- 3D visualization and animation: ArcGIS provides robust 3D visualization capabilities, allowing users to create and analyse data in three dimensions. It also helps to author and share geographic stories as animation videos.
- Web mapping: ArcGIS allows you to create interactive web maps and share them with others, making it easy to collaborate and disseminate information. For example, ArcGIS web map could be used to show how many people in USA live within a reasonable walk or drive to a supermarket.
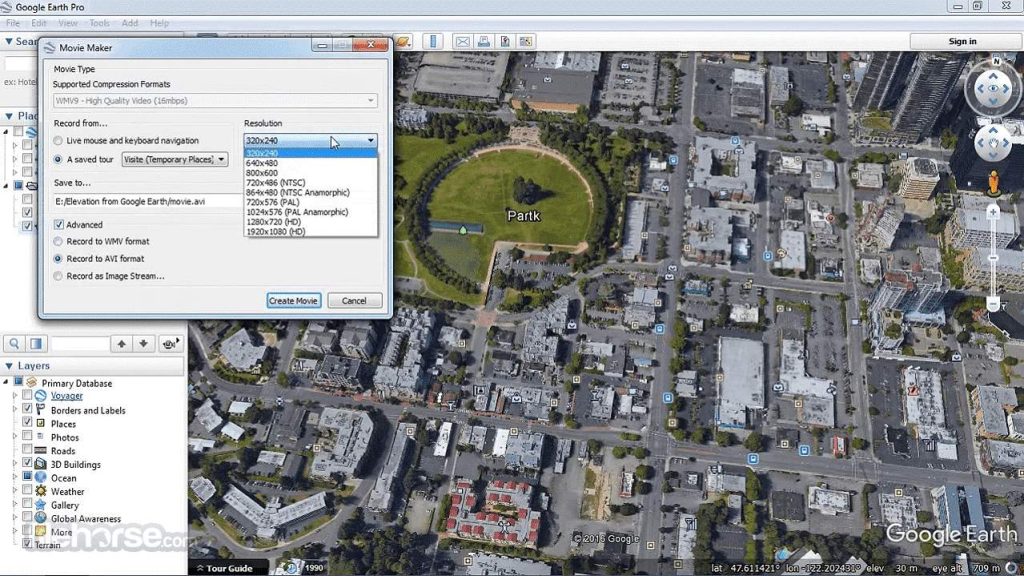
Google Earth Pro
Google Earth Pro’s 3D online mapping system allows you to import and export GIS data, go back in time with historical imagery, analyze and capture geographical data, and create highly detailed maps. It is a free geospatial desktop application that allows you to see the globe and create highly detailed maps according to the location you want.
This resource is extremely user-friendly, making it a helpful intermediary for learners who are interested in gaining more knowledge about GIS but wish to begin with more fundamental procedures and tools.
Google Earth Pro can be used to examine exceptionally high-resolution satellite images, upload or download geographical data in its native interoperable file format (KML), and also discover places by simple geocoding.
Special features of Google Earth Pro include:
- Satellite imagery: Google Earth Pro offers high-resolution satellite imagery, allowing users to view the Earth’s surface in detail.
- Street View: It provides Street View functionality, which allows users to explore locations at street level and view 360-degree panoramas.
- Historical imagery: Google Earth Pro includes historical imagery, enabling users to view past satellite images and compare changes over time.
- Measurement tools: It offers measurement tools that allow users to measure distances, areas, and perimeters on the Earth’s surface.
QGIS 3
QGIS 3 is a free and open-source desktop GIS application that works across multiple platforms and allows users to browse, modify, print, and analyze geospatial data. With QGIS, users can create and edit maps, charts, and diagrams, and select from a number of different symbologies to best represent their data.
This includes spatial analysis features, such as buffer creation, spatial querying, and geoprocessing. Users can also take advantage of plugins and algorithms for further deeper dives into the earth’s geography. Shapefiles, GeoTIFFs, and KML files are just a few examples of the many geographic data formats that may be easily shared and published with QGIS.
Special features of QGIS 3 includes:
- Symbology Interface: QGIS 3 offers a wide range of cartographic styling options, allowing users to create visually appealing maps with customizable symbology.
- Plugin support: QGIS 3 supports many plugins, allowing users to add tools and features. These plugins provide basemaps, advanced digitizing tools, routing services, and geoprocessing tools.
- Digitizing Interface: Its powerful digitizing tool offers CAD-like sketching with shortcuts for selecting line angle and distance, and its construction mode lets you sketch the geometry’s shape.
- Python Integration: Python scripting (Pyqgis) and programming in QGIS 3 lets sophisticated users interact more extensively with GIS layers, geometries, and layouts. Automation and workflow customization require Python capabilities. It is fast and consistent.
AutoCAD Map 3D
The model-based GIS mapping program known as AutoCAD Map 3D provides access to CAD and GIS data in order to assist in the planning, design, and management processes. Utilizing technology known as Feature Data Objects (FDO), it is possible to directly access spatial data. In order to enter precise geometry when building objects, the coordinate geometry (COGO) input commands should be used.
Special features of AutoCAD Map 3D includes:
- CAD integration: AutoCAD Map 3D is built on the AutoCAD platform, providing seamless integration with other AutoCAD products and workflows.
- AEC Industry Specific Functionality: It offers specialized tools and features for the architecture, civil engineering, and construction industry.
- Data conversion: AutoCAD Map 3D includes tools for data conversion, allowing users to import and export data in various formats, making it compatible with other systems. It allows for the data conversion between DWG and GIS data.
- Data visualization: It provides advanced data visualization capabilities, allowing users to create detailed maps and visualizations for analysis and presentation purposes.
BIM and GIS Integration
A GIS map typically converts real-world geographical data into colored patterns or shapes that are more easily perceived by the human eye. This expedites decision-making, which in turn improves the quality of building design choices in the site.
Geographers, surveyors, architects, and other professionals working with geographical mapping can use this technology to create visual representations of a wide range of statistics, such as land planning, demographic information, and more.
To facilitate the digital transformation of the AEC industry, experts will need to merge geospatial and design data. Architects, engineers, and contractors, as well as building owners, can all benefit from BIM and GIS integration. This geographical data with GIS can be integrated with the building design data with BIM and GIS integration.
GIS software like Esri, which pioneered the solution of GIS problems, is now at the forefront of fusing BIM with location intelligence to accelerate development in the building sector.
Esri and Autodesk have joined forces to make GIS and BIM integration the focus of building projects for a more sustainable and resilient future.
The steps involved in BIM and GIS integration involves:
- Data Preparation: Create a GIS geographical model as well as a BIM building or urban design model. The GIS model can be merged with the BIM model using the Autodesk connector for ArcGIS.
- Model Integration: The geographical data as well as the design data are brought together into a single unified model in BIM software like Autodesk Revit.
- Analysis and Design: The contour analysis, daylight analysis, and energy modeling are performed on both the design and the site. Following that, adjustments to the building or urban design, as well as landscape design, are made in the BIM and GIS integrated model.
By choosing the right GIS software that aligns with their specific needs, AEC companies can urban planning, site selection, land use, and master planning in accordance with location data, ultimately leading to successful project outcomes.
BIM and GIS integration, propelled by the latest AI and automation advancements and driven by strict environmental regulations, promises to revolutionize and bring forth innovative solutions in the future for AEC industry.
You may also like to read:
- Ultimate Guide to Create Construction Shop Drawings
- 3D Scanning Software Apps & Technologies in Construction Industry
- Virtual Design & Construction (VDC)
- Robot Structural Analysis: Advanced Design Modeling Solutions
- 5 Ways of Improving the Value of BIM Objects
- 5D BIM Construction for Efficient Planning & Management

Extract quantities for costing and managerial management.
To know more about how we can help you improving your project cost efficacy.
Our Services
Latest Post
Get A Free Quote
BIM Construction is the Future
Building information modeling (BIM) is the future of building design and construction. Get in touch with our BIM Experts.