Think of a world without iconic landmarks like the ‘Colosseum’ or the ‘Taj Mahal’. These historical structures are not just buildings; they are windows into our past, offering invaluable insights into our culture and heritage. Unfortunately, many of these treasures face the constant threat of degradation and loss. That’s where BIM (Building Information Modeling) comes in, playing a crucial role in safeguarding cultural treasures for generations to come.
Table of Contents
ToggleThe Role of BIM in Safeguarding Cultural Treasures
BIM is more than just creating 3D models; it’s a comprehensive digital representation of a building’s physical and functional characteristics. This information-rich model can be used for various purposes, including:
- Detailed documentation: BIM captures every aspect of a heritage structure, from its intricate carvings to its hidden structural elements. This digital archive serves as a permanent record, safeguarding valuable information for future generations.
- Condition assessment and monitoring: BIM models can be used to assess the structural health of heritage buildings and identify potential problems early on. This enables timely intervention and prevents costly damage.
- Virtual restoration and conservation: BIM helps visualize proposed restoration and conservation plans, allowing for meticulous planning and minimizing risks during implementation.
- Improved collaboration: BIM facilitates collaboration amongst architects, engineers, conservators, and other stakeholders involved in heritage projects.
- Engaging storytelling: BIM can be used to create interactive experiences that bring history to life, fostering appreciation for heritage and engaging wider audiences.
Start building a sustainable future today. Get free BIM consultation for your project.
Understanding Heritage BIM: More than Just Digital Models
While BIM offers tremendous benefits, it requires a unique approach when applied to heritage projects. Unlike modern buildings, historical structures often have complex geometries, intricate details, and incomplete or inaccurate documentation. These challenges necessitate specialized workflows and tools tailored specifically for heritage BIM.
Case Studies: European Heritage Meets BIM:
Europe boasts some of the world’s most iconic historical sites, and many countries are actively utilizing BIM to preserve them.
- Italy: The Colosseum in Rome is undergoing a comprehensive restoration project supported by BIM technology. BIM models are being used to document the entire structure, plan restoration works, and monitor the progress of the project.
- France: The Notre Dame Cathedral in Paris suffered a devastating fire in 2019. BIM has been instrumental in the rebuilding process, allowing for accurate reconstruction and preservation of the cathedral’s historic fabric.
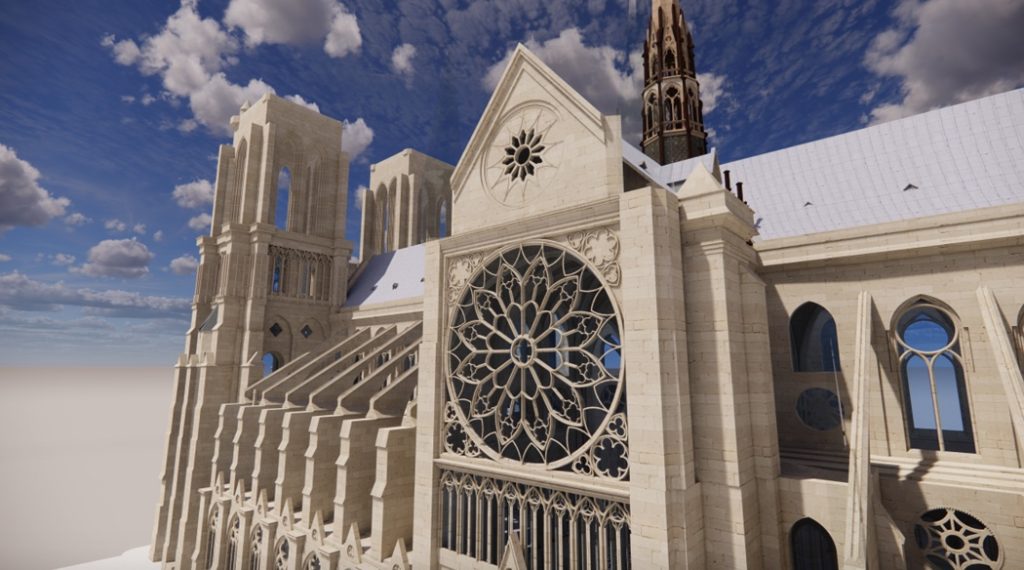

Image Source: autodesk

The meticulously crafted Revit model encompasses not just the majestic Notre Dame itself, but its hidden depths: the crypt, the sacristy, the iconic spire, and even the serene gardens tucked behind the cathedral.
The Extended Reality Project of the Tomb of Caecilia Metella and Caetani Castle:
Immersive Experience through 3D Technology: This project uses 3D technology to create an interactive virtual experience of the Tomb of Caecilia Metella and the Caetani Castle in Rome. It combines 3D scanning, historical reconstruction, and extended reality (XR) to bring these ancient sites to life.
Key features:
- Detailed 3D models: Created using photogrammetry, point clouds, and NURBS algorithms, capturing the intricate details of the historical sites.
- HBIM integration: Building Information Modeling (BIM) provides a platform for managing historical and cultural information within the model.
- Interactive virtual objects (IVOs): Enhance user engagement by allowing interaction with the virtual environment and triggering historical information.
- Open platforms and VPL: The project utilizes open platforms and visual programming languages (VPLs) for developing XR experiences. This enables non-programmers like architects and archaeologists to create interactive content.
- Automatic synchronization: Reduces creation time by automatically syncing models across different software, allowing real-time modelling and interactive development.
- Multiple device compatibility: Accessible on various devices, including workstations, laptops, tablets, mobile phones, and VR headsets.
Benefits:
- Enhances understanding and appreciation of historical sites
- Increases accessibility and engagement for a wider audience
- Provides interactive learning and exploration opportunities
- Preserves cultural heritage for future generations
Overall, this project demonstrates the potential of 3D technology and XR in revolutionizing how we experience and interact with historical sites.

These are just a few examples of how BIM is revolutionizing heritage preservation across Europe.
Victoria Memorial Restoration and Museum Project: A Case Study in India:
This project showcases the power of BIM in conjunction with IoT (Internet of Things) and data analysis. Cameras were used to track visitor movement, providing valuable insights for optimizing visitor flow and ensuring the preservation of the museum’s fragile artifacts.
Digital Documentation of Heritage Structures: BIM as a Digital Time Capsule:
BIM acts as a digital time capsule, capturing the essence of a heritage structure in 3D. This technology allows for precise documentation of:
- Geometry and dimensions: BIM models accurately capture the complex shapes and intricate details of historical structures, providing a detailed record for future generations.
- Materials and finishes: BIM models can store information about the materials used in construction, their condition, and any historical alterations, ensuring their proper conservation.
- Construction techniques: BIM can document historical construction techniques, which are often unique to specific periods and regions, preserving valuable knowledge.
Challenges and Solutions in Documenting Historical Structures:
However, documenting historical structures presents unique challenges:
- Limited access: Certain areas of heritage structures may be inaccessible or unsafe for traditional survey methods.
- Lack of historical documentation: Many historical buildings lack accurate or complete documentation, making it difficult to understand their original design and construction.
- Complex geometries: Historical structures often have intricate shapes and details, requiring specialized tools and expertise for accurate documentation.
BIM technology, combined with advanced laser scanning and photogrammetry techniques, provides solutions to these challenges, enabling accurate and comprehensive documentation of even the most complex historical structures.
Condition Assessment and Monitoring with BIM: Analyzing the Past, Safeguarding the Future:
BIM empowers heritage professionals to:
- Analyze structural health: BIM models can be used to perform structural analysis, identifying potential problems such as cracks, deformations, and material deterioration.
- Monitor changes over time: By integrating sensors with BIM models, heritage professionals can monitor changes in temperature, humidity, and other environmental factors that can affect the building’s condition.
- Predict future deterioration: BIM models can be used to predict how a heritage structure will deteriorate over time, allowing for preventative measures to be taken before significant damage occurs.
Real-time Monitoring: Using BIM to Safeguard Fragile Structures:
Real-time monitoring with BIM sensors is crucial for safeguarding fragile structures, especially in earthquake-prone regions. These sensors can detect even the slightest movements and vibrations, providing early warning of potential dangers and facilitating rapid intervention. This real-time data can be integrated into BIM models, allowing for proactive conservation efforts and ensuring the long-term preservation of these treasured structures.
BIM in Restoration and Conservation
Virtual Restoration: How BIM Helps Bring Heritage Sites Back to Life?:
BIM empowers heritage professionals to virtually reconstruct historical buildings to their former glory. This enables them to:
- Visualize proposed restoration plans: BIM helps visualize proposed restoration plans in detail, allowing stakeholders to assess their impact before any physical work begins.
- Minimize risks during restoration: By creating virtual simulations, BIM can identify potential problems and conflicts during the restoration process, minimizing risks and ensuring a smooth execution.
- Preserve historical accuracy: BIM allows for the accurate reconstruction of missing or damaged elements, ensuring the authenticity of the restored structure.
Conservation Challenges: BIM Solutions for Preserving Authenticity:
One of the main challenges in heritage conservation is ensuring authenticity. BIM offers several solutions:
- Material and technique databases: BIM platforms can integrate databases of historical materials and construction techniques, guiding restoration efforts towards authenticity.
- Reversibility: BIM models can document the original state of a structure and any modifications made during restoration, allowing for future restoration and ensuring the reversibility of interventions.
- Heritage impact assessment: BIM can be used to assess the potential impact of proposed interventions on the historical significance and authenticity of a heritage site.
Collaboration in Heritage Projects:
Teamwork in Time Travel: Collaborative Heritage Preservation with BIM:
BIM facilitates seamless collaboration between various stakeholders involved in heritage projects, including:
- Architects and engineers
- Conservators and historians
- Construction workers and craftspeople
- Local communities and government agencies
By working with a single, shared BIM model, these stakeholders can effectively communicate, coordinate their efforts, and achieve optimal results in heritage preservation projects.
Breaking Silos: Interdisciplinary Collaboration in BIM for Heritage:
BIM breaks down traditional silos between disciplines, fostering interdisciplinary collaboration and knowledge sharing. This collaboration enables:
- Holistic approach to preservation: By considering architectural, historical, and engineering perspectives simultaneously, BIM ensures a holistic approach to heritage preservation.
- Improved decision-making: Interdisciplinary collaboration leads to informed decision-making, ensuring that preservation efforts are effective and sustainable.
- Enhanced understanding of heritage: BIM facilitates the exchange of knowledge and understanding between different disciplines, leading to a deeper appreciation of our heritage.
Showcasing Heritage in the Digital Age:
Heritage Storytelling: Communicating History through BIM:
BIM empowers creative storytelling that brings history to life. Through interactive 3D models, virtual tours, and augmented reality experiences, BIM can:
- Engage wider audiences: BIM makes heritage accessible and engaging for a wider audience, fostering appreciation for history and cultural heritage.
- Educate and inform: BIM can be used to create educational resources that provide valuable information about historical sites and artifacts.
- Promote cultural exchange: BIM can be used to share heritage stories with people around the world, fostering intercultural understanding and appreciation.
Virtual Tours and Augmented Reality: Making Heritage Accessible:
Virtual tours and augmented reality (AR) experiences powered by BIM can make heritage sites accessible to everyone, regardless of physical limitations or geographical location. These technologies allow visitors to:
- Explore historical sites remotely
- Interact with 3D models and historical artifacts
- Gain insights into the history and construction of heritage buildings
By making heritage accessible and engaging, BIM can inspire future generations to become stewards of our shared past.
Wrapping Up:
As technology continues to evolve, BIM offers immense potential for safeguarding our cultural heritage. By embracing BIM’s ability to document, analyze, restore, and showcase heritage sites, we can ensure their preservation for future generations. Let us continue to innovate and collaborate for a future where the past is not only remembered but also cherished and celebrated.
Further Reading
What Is BIM? Guide To Implementation And Myths
The Future Of BIM Construction- Trends, Challenges & Adoption
4 Stages Of BIM Process In Building Construction
Key Benefits And Role Of BIM Design In Construction
Applications Of BIM Technology In The Construction Industry
BIM LOD (Level Of Development)- 100 200 300 350 400 500
Our Services
Latest Post
Get A Free Quote
BIM Construction is the Future
Building information modeling (BIM) is the future of building design and construction. Get in touch with our BIM Experts.