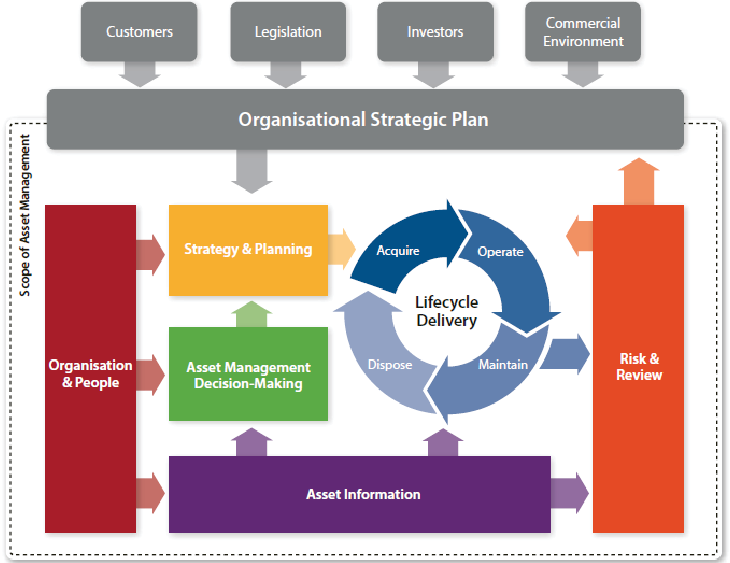
BIM Asset Management is defined as the strategic approach to managing project assets to facilitate the attainment of business goals for construction projects.
Table of Contents
ToggleBIM (Building Information Modeling) enhances asset management by converting building management goals into decisions, plans, and activities that pertain to the asset. This facilitates the realization of value from the asset.
BIM Asset management operations offer AEC industry organizations a strategic framework, a collection of processes, methodologies, and tools. That enable them to address the increasing expectations from stakeholders, deteriorating asset base, or limited funds.
The Relationship Between BIM and Asset Management
BIM and asset management to date have concentrated on the design and construction stages of assets in the construction industry. It is increasingly becoming clear that BIM can and should be used throughout the entire asset life cycle.
It is thus a crucial enabler of better management of assets within the internationally recognized ISO55000 framework.
The 5th dimension of BIM is related to asset management. The 4D BIM scheduling, 5D BIM cost estimation and Quantity Take Off (QTO), 6D BIM sustainability analysis, and 7D BIM facility management help in streamlining the BIM Asset Management process.
In the following three cases, BIM and Asset Management need to complement each other:
- Implementing BIM for previously existing assets
- Utilizing BIM to create brand new assets
- Using BIM to operate and manage both existing assets and new ones.
Difference Between Asset Management and Facility Management
While BIM Asset Management and BIM Facility Management share many similarities, there are important distinctions between the two that must be taken into account. What assets are managed and how they are managed are essentially the primary distinctions between AM and FM.
Let us take a look at the key distinctions between asset management and facility management:
- While the focus of asset management is on the function and utility of individual assets, the scope of facility management extends to the entire physical space and all the equipment and other assets within it.
- The purpose of asset management is to increase an organization’s long-term profit from its physical assets. The goal of facility management is to maintain a high level of functionality for the benefit of those who occupy the physical space.
- Asset management measures include Return on Investment (ROI), total cost of ownership, and asset usage. Facility management uses different KPIs including work orders, program status, asset condition, and maintenance.
Adoption of BIM-enabled Asset Management
From design until handover, the entire asset lifespan can be monitored and managed in one convenient location with the help of the new BIM 360 asset management module.
The Asset Manager requires access to the correct data in order to make decisions that lead to actions—including data updates—while minimizing risk.
Field teams can benefit from these features because they shorten the time it takes to access asset data in the field, perform commissioning, and resolve defects.
BIM can be used to collect and manage a wide variety of data, such as:
- Asset register or inventory information
- Topographic data on the assets
- Indicators of asset condition
- Data on the assets’ potential uses
- Measures of asset efficiency such as uptime, failure rates, and other metrics
- Information on how long various types of machinery and supplies tend to last
- Descriptions and costs of potential interventions for upkeep and refurbishment
- Location-based information, such as weather and topography
- Things that have happened to the asset in the past, like maintenance, alterations, renewals, and replacements; and things that have gone wrong, like accidents.
Using manufacturer-specific data, BIM objects of assets are created so that building services can be tracked and managed in the field with BIM asset management.
BIM Asset Information Requirements (AIR)
As part of the Building Information Modeling (BIM) procedure, Asset Information Requirements (AIR) are developed to specify the visual and non-visual data, information, and documentation required for the lifetime operation and management of a built asset.
The asset information needs will be laid out in a document titled Asset Information Requirements (AIR). In accordance with the organization’s broader asset management plan, as stated in the Organizational Information Requirements (OIR).
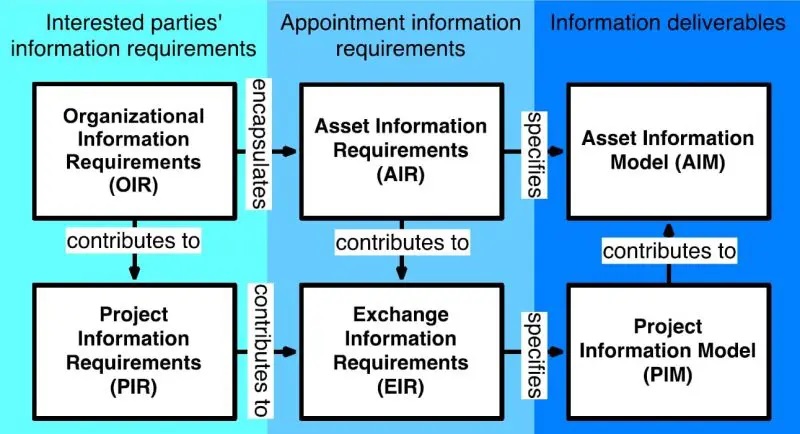
This document will outline the requirements for the provision and administration of information about a built asset.
Once the needs for asset data are established, an Asset Information Model (AIM) can be developed.
The AIM is all the data and information collected in response to the AIR, so it has everything the asset manager needs to run and maintain the asset over its lifetime.
Benefits of BIM in Asset Management
An asset manager can immediately find the cause of the problem and the need to remedy it with the help of a 3D BIM model for asset management. The benefits of BIM for asset management are:
- Accurate asset planning for streamlined repairs, maintenance, remodeling, and renovation: BIM can generate a 3D model of an asset’s geometry, materials, and specifications, called a digital twin. This data can help plan asset maintenance, repairs, and upgrades. BIM models can recognize regions of an asset in danger of wear and tear to schedule preventive maintenance.
- Energy efficiency and sustainability: BIM can evaluate asset energy efficiency and suggest improvements. This data can help sustainably manage assets. BIM models can indicate parts of an asset that lose heat or energy, allowing insulation or other energy-saving measures to be adopted.
- Effective resource allocation: BIM asset management considers the complete asset lifecycle, from design and construction through disposal and recycling. This data can optimize resource allocation throughout the asset’s lifecycle, saving cost and resources.
- Supports BIM facility management: Integrating BIM with FM technologies can automate and streamline asset management. This improves efficiency, cuts expenses, and frees up staff time. FM employees can concentrate on arranging and executing maintenance tasks when a BIM model automatically generates work orders.
BIM in Asset Management: Adoption, Benefits & Differences
Integrating the idea of the digital twin into a framework for the creation of future intelligent asset management is advocated.
The digital twin is an integration of artificial intelligence, machine learning, and data analytics that is used to generate dynamic digital models that are able to learn and update the state of the physical counterpart from many sources.
The findings will help to contribute to the general use of smart digital twin enabled BIM asset management systems throughout the facilities operations and maintenance phase.
The business value of integrated BIM-based asset management is considerably more than the traditional asset management system.
BIM 360 asset management provides you with the tools you need to track all of your project’s assets and equipment from design to handover.
You may also like to read:

Schedule an appointment with the BIM Consultants of TopBIM Company
To know more about how we can help you improving your project cost efficacy.
Our Services
Latest Post
Get A Free Quote
BIM Construction is the Future
Building information modeling (BIM) is the future of building design and construction. Get in touch with our BIM Experts.