3D Scanning Of Buildings For Architecture, Engineering, & Construction (AEC)
- Home
- Blog

What is 3D Laser Scanning of Buildings?
3D laser scanning is a technology used to create highly detailed and accurate digital models of physical structures. It involves using a laser scanner to capture millions of data points from the surface of a building, which are then processed to create a three-dimensional model of the structure.
Table of Contents
ToggleThe resulting 3D model can be used for a variety of applications, including building information modeling (BIM), architectural and engineering design, construction planning and monitoring and heritage preservation.
History of 3D Laser Scanning in Construction
| Year | Technological Advancement | Adoption Rate | Key Applications |
| 1960s | Early development of 3D scanning technology using lights, cameras, and projectors. | Limited | Topographical surveying, industrial applications. |
| 1970s | Introduction of terrestrial laser scanners (TLS). | Minimal | As-built documentation, historical preservation. |
| 1980s | Advancements in laser technology and data processing capabilities. | Gradually increasing | Construction layout, clash detection, volume measurement. |
| 1990s | Introduction of airborne laser scanning (ALS) and mobile laser scanning (MLS). | Slowly gaining traction | Infrastructure projects, large-scale site surveys, building renovations. |
| 2000s | Integration of BIM software with laser scanning data. | Significant growth | Prefabrication, quality control, 4D BIM modeling. |
| 2010s | Development of high-resolution scanners and real-time data processing. | Widespread adoption | Facility management, asset tracking, safety planning. |
| 2020s | Integration of AI and machine learning for automated data analysis. | Nearly ubiquitous | Robotics, autonomous construction, digital twins. |
Reality Capture of Building using 3D Laser Scanning
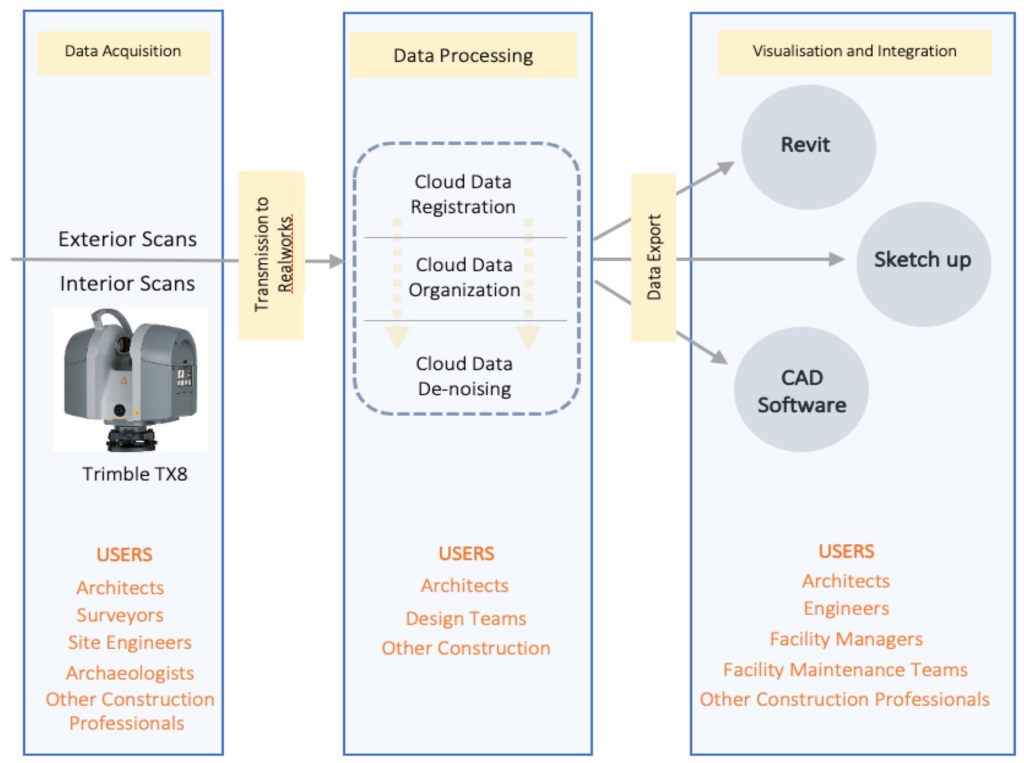
Image Source: mdpi.com
Using intelligent 3D models that are accurate and accessible, 3d scanning of buildings has enhanced the way professionals in the architecture, engineering, and construction (AEC) industries collaborate.
Drones, UAVs, terrestrial scanners, and digital Photogrammetry are just a few of the constantly developing 3D scanning technologies that enable mapping virtually of every area of a construction site with previous levels of detail.
Scanning technology using 3D scanner for building can be used for many kinds of projects, including new building, during the construction process. This provides an extremely accurate and up-to-date record of site progress, with benefits for cost, build quality, and delivery.
3D Building Scanning Market Size and Growth Forecast
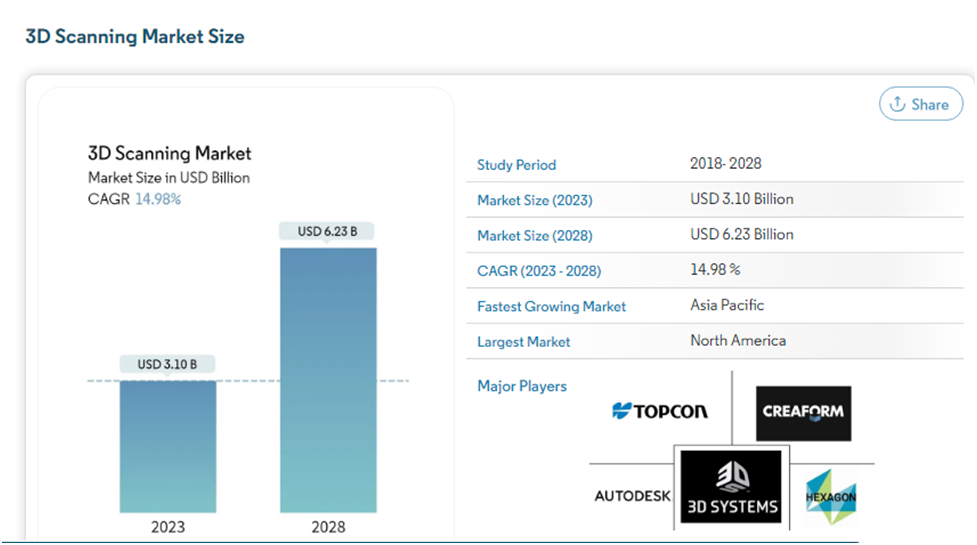
Source: Mordor Intelligenece
The 3D Scanning Market is on track for significant expansion, set to increase from USD 3.10 billion in 2023 to a formidable USD 6.23 billion by 2028. This growth reflects a compelling CAGR of 14.98% over the forecast period (2023-2028)..
Although 3D scanning technology has not been widely adopted in residential and private settings, other industrial sectors, such as architecture, construction, aerospace, healthcare, and automotive, have found considerable use for this technology.
- The demand for laser scanning is increasing in the construction industry and is expected to grow by $10 billion by 2024.
- Healthcare, aerospace and defence, architecture and engineering, 3D Digital Corporation, research and education, entertainment, and media are some of the most significant, largest, and technologically advanced 3D scanning industries in the United States, making it one of the most important and consequential 3D scanning markets in the world.
- As Canada is committed to ensuring that everyone has access to healthcare, the government spends more than 10% of its GDP on healthcare, one of the highest percentages in the industrialized world, which translates to well over USD 5000 in expenditure on the healthcare industry per capita.
Building Laser Scanning Process Explained
Building laser scanning is more than just a technology; it’s a paradigm shift in how we approach existing structures. By bridging the gap between physical buildings and their digital representations, it empowers us to build, renovate, and preserve with greater precision, efficiency, and insight. Building scanning captures and analyzes existing structures.
The following four-step process guarantees detailed, accurate data for informed decision-making.
- Site Planning: Before beginning the scanning process, it’s important to plan and prepare for the project. This may involve selecting the appropriate type of laser scanner for the job, determining the scanning locations and viewpoints, and coordinating with stakeholders to ensure access to the building and any necessary permits.
- Laser Scanning: Once the scanner is set up, it emits laser beams that sweep across the building’s surfaces, capturing millions of data points. The scanner is moved or repositioned as necessary to capture data from different viewpoints and angles.
- 3D Model creation: The point cloud data is then used to create a 3D model of the building, which can be manipulated and viewed from any angle. The model can also be annotated with additional information, such as material properties or construction details.
- Model Analysis and application: The 3D model can be used for a variety of purposes, such as visualization, simulation, and analysis. It can also be integrated with other software and tools, such as BIM or GIS, to support the design, construction, and maintenance of the building.
The advantages of laser scanning in construction
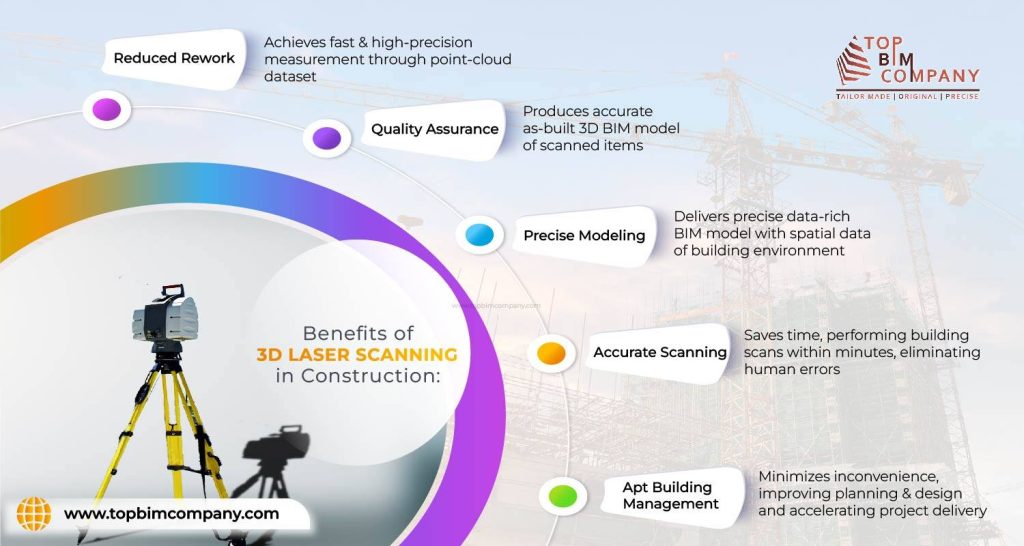
- Reduced Rework: Rework can add up to 15% of the cost of a building project on an average. However, routine 3D scanning can identify any possible problems before they result in change orders, lowering risk for the principal contractor.
- Quality Assurance: By scanning at predetermined intervals, it is able to record important milestones like hand-offs between trades and compare completed work to models and drawings that reflect the original design for quality assurance.
- Precise Modeling: A thorough building 3D laser scanning survey essentially creates a copy of the structure at the time of the scan. It could mean that subcontractors have complied with the deliverables of the contract. It maintains the integrity of the contractors and significantly lowers modification orders, which usually result from projects that are poorly documented without laser scanning.
- Accurate Scanning: To confirm that all components are installed in the proper positions, millimeter-accurate scan data on plumbing, HVAC, structural steel, structural rebar detailing in concrete, etc. that is tagged with actual installation dates may be compared to the design. In the event that mistakes are found, it might be possible to modify the design and create new components rather than having to perform corrective work on-site.
- Building Management: Clients and building owners can gain from having a record of what is located beneath the floor slabs, above the ceilings, and behind the walls. They might utilize it for building management and upkeep after handover or as the foundation for later refurbishment work.
For quality assured 3D Laser Scanning of your project
Our BIM Professionals will provide a customized solution & cost estimation for your project.
Tools & techniques used in laser scanning for building surveying
Although general contractors frequently hire specialized surveying companies to handle their laser scanning needs, many choose to manage task themselves by renting or buying their own laser scanner and software.
- The scale of the project, the type of data that must be defined, and the speed and regularity of survey completion will all affect the choice of the best tools for the work.
- The most accurate 3D scanner for buildings can capture very thick point clouds on the ground. These digital images of the space in three dimensions were created using a vast number of data points, such as X, Y, and Z coordinates, color values, and reflectance values. BIM software may import such point cloud data.
- Unmanned aerial systems (drones) can be used to capture point clouds by stitching together high-resolution photos of the topography, building exteriors, and difficult-to-reach locations on roofs.
- Projects that need to quickly and frequently collect high-quality data to update as-built information might greatly benefit from a mobile mapping system like the NavVis M6 cart.
- The M6 can gather 100,000 to 150,000 square feet of data every day, as opposed to 25,000 square feet using a tripod scanner, and is up to 10 times faster than static scanning equipment. This is especially helpful when a surveyor only has a short window of opportunity to access a busy construction site.
- The M6 also incorporates the newest 6D SLAM (Simultaneous Localization and Mapping) technology, which is particularly important in challenging areas like construction sites and is designed to reliably gather data on uneven surfaces.
Building Laser Scanning Adoption Challenges
- It’s expensive: Building laser scanning can be an expensive process, particularly for larger or more complex buildings. This may make it difficult to justify the use of the technology for certain projects.
- Experience is required: Workers have to undergo rigorous training on how to use the technology effectively, just like any other technology.
How to Start Implementing Laser Scanning in Construction?
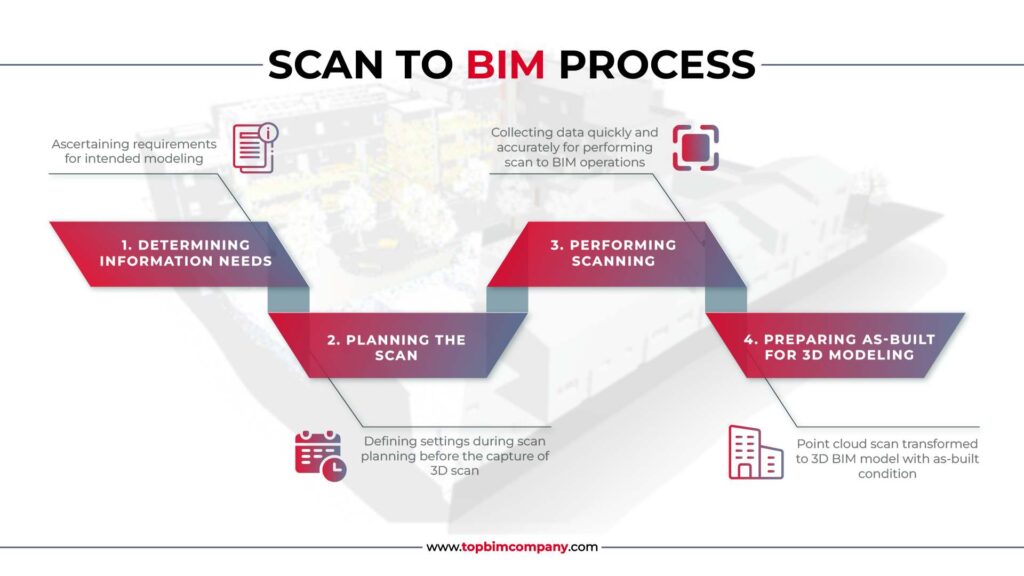
To start implementing laser scanning in construction, there are a few steps to follow:
Determine the scope of your project: First, you need to determine the scope of your project and identify areas where laser scanning can be used. This could include site surveys, as-built documentation, quality control, and monitoring construction progress.
Evaluate your equipment needs: Determine the type of laser scanner you need for your project, as well as the software required to process and analyze the captured data. You may also need to invest in supporting equipment such as tripods, targets, and laptops.
Hire a qualified surveying team: It’s essential to hire a qualified surveying team with experience in laser scanning to ensure accurate and reliable results. Look for professionals who are trained in using laser scanners and have a proven track record in delivering successful projects.
Develop a project plan: Develop a detailed project plan that includes timelines, budget, and goals. This will help ensure that the project runs smoothly and that you achieve your objectives.
Implement laser scanning on site: Once you have everything in place, it’s time to implement laser scanning on site. This involves setting up the equipment, scanning the site, and processing the captured data.
Analyze and share data: Finally, you’ll need to analyze and share the data captured through laser scanning with stakeholders such as architects, engineers, and construction teams. This can help improve collaboration and communication and ensure that everyone is on the same page regarding project progress and quality control.
Transform Construction Projects with 3D Laser Scanning
3D laser scanning of buildings is a powerful tool that can help architects, engineers, and construction professionals to better understand and analyze the built environment, and to make more informed decisions throughout the design, construction, and maintenance process.
Constantly evolving 3D scanning techniques, including drones, UAVs, terrestrial scanners and digital photogrammetry, make it possible to map almost every corner of a construction site at an unprecedented level of detail.
Construction teams all around the world are beginning to recognize the speed and accuracy advantages of laser scanning over conventional surveys, and the possibilities are nearly unlimited when the results are brought into BIM.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs):
Question: Why is 3D scanning important for existing buildings?
Answer: 3D scanning captures accurate geometry of existing structures, eliminating assumptions and enabling precise BIM models. This accuracy is critical for renovation and retrofit planning.
Question: How does 3D scanning support renovation and retrofit projects?
Answer: It provides exact measurements of existing conditions, reducing design risk, minimizing rework, and improving construction confidence.
Question: What technologies are commonly used for building scans?
Answer: Terrestrial laser scanning, LiDAR, and photogrammetry are widely used to capture high-resolution spatial data in the AEC industry.
Question: Which industries benefit most from building scanning?
Answer: Construction, heritage preservation, industrial facilities, and facility management teams gain the most value from 3D scanning.
Question: What challenges are associated with 3D scanning data?
Answer: Large data volumes, complex processing requirements, and the need for skilled specialists can pose challenges during implementation.
You would like to explore our services
Our Services
Latest Post
Get A Free Quote
BIM Construction is the Future
Building information modeling (BIM) is the future of building design and construction. Get in touch with our BIM Experts.





